EV, HEV, and PHEV: What’s the Difference?
There are several types of electric vehicles out on the market, and understanding their differences is important, especially if you are considering purchasing one. There are three main types, and they are:
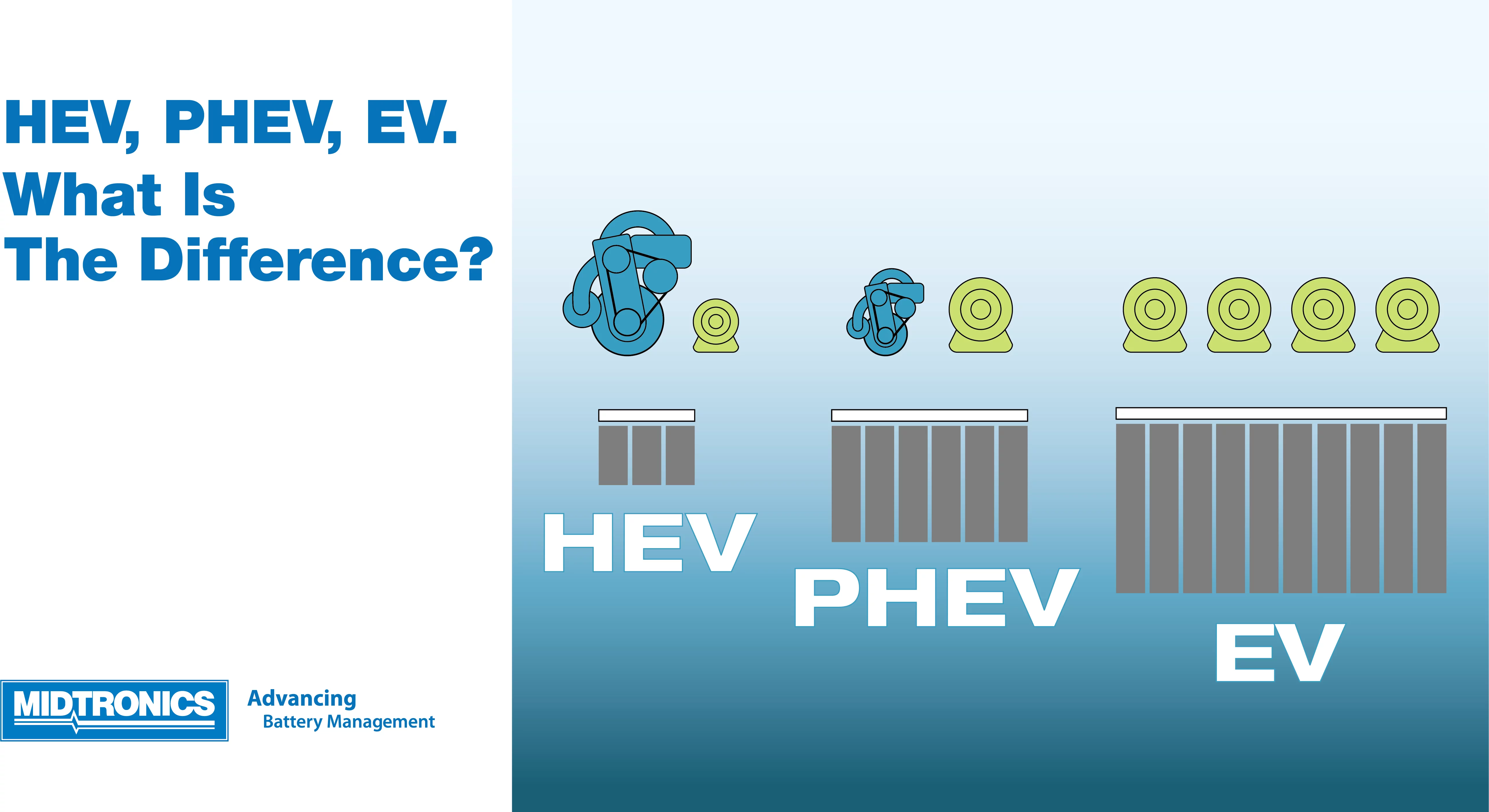
EV – Electric Vehicle, also known as a Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
HEV – Hybrid Electric Vehicle
PHEV – Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle
Below we will go into more detail explaining the above and their differences, as well as their maintenance needs.
EV (Electric Vehicle)
An Electric Vehicle (EV) is a fully electric vehicle that has rechargeable batteries. These batteries are recharged from the grid and are the only source of power for the vehicle, as they do not have a tank for gasoline. When referring to these vehicles, they are also called a BEV.
HEV (Hybrid Electric Vehicle)
Hybrid Electric Vehicles are both electric and gas-powered. The energy that powers their batteries is gained through regenerative braking or while driving using the combustion engine. In a standard gas-powered car, the energy from the braking is lost in the form of heat. This happens by way of the rotors and brake pads. The grid cannot charge these types of electric vehicles.
PHEV (Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle)
PHEVs have both an engine and an electric motor. Like a regular hybrid, PHEVs can recharge their batteries through regenerative braking or with the engine. The primary difference between an HEV and a PHEV is the addition of a charging port into the PHEV. In this way, a PHEV can operate more like a EV, driving off the battery and recharging off the grid, only using the combustion engine when the battery is depleted. PHEV batteries are typically higher capacity than HEV batteries.
Another difference is the distance they can travel before their gas engines turn on. A PHEV will run anywhere from 10 to 40 miles, whereas an HEV will only run less than 2 to 3 miles.
All of the above vehicles will require maintenance for their batteries, also called energy storage systems. To learn more, continue reading below.
Energy Storage System Types
Batteries are essential to EVs, HEVs, and PHEVs. There are lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride, and lead-acid energy storage systems. In addition to the above, there are also ultracapacitors that are used to provide additional power during acceleration.
Maintenance and Recycling Batteries
To maintain these vehicles, it is important to have them regularly checked per the car manufacturer. So the question most commonly asked is, do EVs require extra vehicle maintenance? The answer to that question is no.
Electric Vehicle Maintenance
Powertrain: Most EV, HEV, and PHEV vehicle manufacturers offer long warranties on powertrains, which speaks to their lasting reliability. The powertrain is simple and requires little maintenance (replacing fluid) when compared to gas-powered vehicles.
Brakes: With the regenerative braking system, brake wear is lower for those that rely on friction braking. However, components of friction braking such as rotors, pads, and brake fluid will still need to be replaced at some point.
Cooling: The energy storage systems on these vehicles use a coolant or refrigerant to keep key parts (charger, inverter, and battery pack) cool. Therefore, maintenance for cooling systems may require infrequent coolant flushes to help the vehicle’s efficiency.
Batteries: As for the maintenance of EV batteries, it is more about prolonging their life. Over time the packs will degrade, and the ability to hold a charge will decrease gradually. To prolong the life of these batteries, you can do the following:
- In storage and in use, minimize high and low temperatures
- Minimize the urge to want to stay at a 100% state of charge/Don’t stay at 0% for very long either
- Although convenient, avoid fast charging
- Avoid storage in high moisture areas
- Avoid damage to mechanical components
- Ultimately, be sure to follow the manufacturer’s calibration instructions/This will often require you to complete an initial full discharge
EV vs. HEV and PHEV Maintenance
When comparing all three electric vehicle types, we can see that the HEV and the PHEV will require more maintenance because it has a conventional combustion engine and an electric drivetrain. However, overall, the maintenance is significantly less when put up against an internal combustion engine.
Recycling EV Batteries
As with all batteries, they do have a life cycle and will need to be recycled. The recycling process for EV batteries typically involves recovering the individual parts and materials of the battery so as not to release hazardous toxins into the environment.
Since the EV market is fairly new, most EVs have yet to reach that point. Therefore, recycling these batteries is still undergoing research; while some manufacturers are reusing the batteries in their plants, others are opening recycling facilities